Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Shigeru; Meigo, Shinichiro; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Hirano, Yukinori*; Tsutsumi, Kazuyoshi*; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Technology 2023-025, 48 Pages, 2024/03
JAEA has been developing Accelerator-Driven Systems (ADS) for research and development of nuclear transmutation using accelerators in order to reduce the volume and hazardousness of high-level radioactive waste generated by nuclear power plants. In order to prepare the material irradiation database necessary for the design of ADS and to study the irradiation effects in Lead-Bismuth Eutectic (LBE) alloys, a proton irradiation facility is under consideration at J-PARC. In this proton irradiation facility, 250 kW proton beams will be injected into the LBE spallation target, and irradiation tests under LBE flow will be performed for candidate structural materials for ADS. Furthermore, semiconductor soft-error tests, medical RI production, and proton beam applications will be performed. Among these, Post Irradiation Examination (PIE) of irradiated samples and RI separation and purification will be carried out in the PIE facility to be constructed near the proton irradiation facility. In this PIE facility, PIE of the equipment and samples irradiated in other facilities in J-PARC will also be performed. This report describes the conceptual study of the PIE facility, including the items to be tested, the test flow, the facilities, the test equipment, etc., and the proposed layout of the facility.
 Pb and
Pb and  Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeV
Bi in proton-induced reactions near 100 MeVIwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Yashima, Hiroshi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Sugihara, Kenta*; 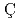 elik, Y.*; et al.
elik, Y.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 544, p.165107_1 - 165107_15, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)The lack of double-differential cross-section (DDX) data for neutron production below the incident proton energy of 200 MeV hinders the validation of spallation models in technical applications, such as research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs). The present study aims to obtain experimental DDX data for ADS spallation target materials in this energy region and identify issues related to the spallation models by comparing them with the analytical predictions. The DDXs for the (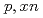 ) reactions of
) reactions of  Pb and
Pb and  Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30
Bi in the 100-MeV region were measured over an angular range of 30 to 150
to 150 using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
using the time-of-flight method. The measurements were conducted at Kyoto University utilizing the FFAG accelerator. The DDXs obtained were compared with calculation results from Monte Carlo-based spallation models and the evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-5. Comparison between the measured DDX and analytical values based on the spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library indicated that, in general, the CEM03.03 model demonstrated the closest match to the experimental values. Additionally, the comparison highlighted several issues that need to be addressed in order to improve the reproducibility of the proton-induced neutron-production DDX in the 100 MeV region by these spallation models and evaluated nuclear data library.
Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi*
Ten Hasseigen Karano Mesosukeru Kakusan Shumireshon; Fukushima Daiichi Genshiryoku Hatsudensho Jiko O Fumaete (Kisho Kenkyu Noto Dai-248-Go), p.1 - 58, 2023/09
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.435 - 449, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Double-differential thick target neutron yields (TTNYs) for Fe, Pb, and Bi targets induced by 107-MeV protons were measured using the fixed-field alternating gradient accelerator at Kyoto University for research and development of accelerator-driven systems (ADSs) and fundamental ADS reactor physics research at the Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). Note that TTNYs were obtained with the time-of-flight method using a neutron detector system comprising eight neutron detectors; each detector has a small NE213 liquid organic scintillator and photomultiplier tube. The TTNYs obtained were compared with calculation results using Monte Carlo-based spallation models (i.e., INCL4.6/GEM, Bertini/GEM, JQMD/GEM, and JQMD/SMM/GEM) and the evaluated high-energy nuclear data library, i.e., JENDL-4.0/HE, implemented in the particle and heavy iontransport code system (PHITS). All models, including JENDL-4.0/HE, failed to predict high-energy peaks at a detector angle of 5 . Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of
. Comparing the energy- and angle-integrated spallation neutron yields at energies of  20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
20 MeV estimated using the measured TTNYs and the PHITS indicated that INCL4.6/GEM would be suitable for the Monte Carlo transport simulation of ADS reactor physics experiments at the KUCA.
Saito, Shigeru; Yamaguchi, Kazushi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; Obayashi, Hironari; Sasa, Toshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2022-032, 51 Pages, 2023/03
In the Accelerator Driven System (ADS) being studied by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) for transmutation of long-lived radioactive waste, lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is used as a spallation target and subcritical core coolant. A proton irradiation facility in J-PARC is considered to prepare a material irradiation database for ADS development. The proton irradiation facility is equipped with an LBE loop, which enables material irradiation tests in spallation environment under flowing LBE condition. The slow leakage of LBE is one of critical issue to use LBE safety. The slow leakage is caused by the biting slag and/or other materials at valve seal of drain valve. To solve this problem, JAEA examined the application of freeze-seal valve (FSV), which seal the piping by freezing LBE in specific position. Water-cooled and air-cooled freeze-seal valve test modules were fabricated, installed in the test section of the existing test stand for LBE technology development, and tested to confirm their operation and performance. As a result of the tests, it was confirmed that the water-cooled FSV test module worked well along to the design values. This report describes the outline and details of the test stand for LBE technology and each FSV test module, as well as the results of operation and performance verification tests.
Murakami, Hiroaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iwatsuki, Teruki
JAEA-Technology 2022-022, 34 Pages, 2022/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting the hydro-pressure and hydrochemical monitoring for more than two decades to understand the hydrochemical disturbance due to the excavation of tunnels at Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). To understand the environmental influence due to the backfilling of research tunnels that started in 2019, environmental monitoring of groundwater has been performed and recovery status of groundwater is being confirmed. In order to observe the deep-groundwater environment from the ground, the groundwater pressure monitoring and sampling, which have been performed in the research tunnel, are to be performed from the ground. However, backfilling of a large-scale underground facilities such as MIU is globally unprecedented, thus it was necessary to develop a new observation system. Accordingly, we developed a new observation network to observe the environment around the research tunnels of the MIU. This system enables monitoring of groundwater pressure and water sampling of the backfilled tunnel from the ground while utilizing the existing-monitoring system installed in the tunnels. Accordingly, we demonstrated its technology through the environmental monitoring of groundwater. The results of the environmental monitoring and the existing groundwater data of MIU indicate that this system is able to monitor the groundwater environment in the backfilled tunnels.
Kato, Atsushi; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Ando, Masato; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Murakami, Hisatomo*; Oyama, Kazuhiro*; Kaneko, Fumiaki*; Higurashi, Koichi*; Chanteclair, F.*; Chenaud, M.-S.*; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 8, p.11_1 - 11_10, 2022/06
This paper provides an overview of plant system studies to establish a common technical view for Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor concept between France and Japan based on ASTRID600 and the new concept with downsized output called ASTRID150. One of important issues on a reactor structure design is to enhance seismic resistance to be tolerable against strong earthquake such that postulated in Japan. A concept of High Frequency Design is shared, and the design options related to HFD have been examined and design recommendations are established. In addition, this paper include results of studies for a steam generator, a decay heat removal system, a fuel handling system and a containment vessel.
Sato, Yuki
Isotope News, (781), p.19 - 23, 2022/06
no abstracts in English
Sato, Yuki
Kensa Gijutsu, 27(5), p.9 - 15, 2022/05
no abstracts in English
Saito, Shigeru; Wan, T.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Kita, Satoshi*; Obayashi, Hironari; Sasa, Toshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2021-034, 94 Pages, 2022/03
Lead-bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is a major candidate for a spallation target material and core coolant of an accelerator driven system (ADS) which has been developed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to transmute high-level radioactive wastes. A proton irradiation facility to build a material irradiation database for future ADS development is under considering in the J-PARC. To realize both the ADS and the above-mentioned facility, there are many issues on operational safety of LBE to be solved. Especially, corrosion data for the major materials such as T91 (Modified 9Cr-1Mo steel) and SS316L at the temperature range between 400 and 550  C under the conditions of flowing LBE with a controlled oxygen are not sufficient to design the ADS and the facility. JAEA developed a new large-scale corrosion test loop named "OLLOCHI (Oxygen-controlled LBE LOop for Corrosion tests in HIgh-temperature)" aiming to perform the compatibility tests between the LBE and the steels, as well as to develop the LBE operation technology. OLLOCHI has a function to automatically control the oxygen concentration in LBE. The maximum temperature at the regions of high-temperature and low-temperature of the OLLOCHI are 550
C under the conditions of flowing LBE with a controlled oxygen are not sufficient to design the ADS and the facility. JAEA developed a new large-scale corrosion test loop named "OLLOCHI (Oxygen-controlled LBE LOop for Corrosion tests in HIgh-temperature)" aiming to perform the compatibility tests between the LBE and the steels, as well as to develop the LBE operation technology. OLLOCHI has a function to automatically control the oxygen concentration in LBE. The maximum temperature at the regions of high-temperature and low-temperature of the OLLOCHI are 550  C and 450
C and 450  C respectively to cover the ADS designed condition. As a result of 2,000 hours operation, it was demonstrated that the OLLOCHI showed the designed performance. In this report, outline of the OLLOCHI, details of the components, results of characteristic tests, and the future experimental plan are described.
C respectively to cover the ADS designed condition. As a result of 2,000 hours operation, it was demonstrated that the OLLOCHI showed the designed performance. In this report, outline of the OLLOCHI, details of the components, results of characteristic tests, and the future experimental plan are described.
Katano, Ryota; Nishihara, Kenji; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Meigo, Shinichiro
JAEA-Research 2021-016, 16 Pages, 2022/03
It has to be confirmed that the accelerator-driven system (ADS), which is dedicated to transmuting minor actinides, is subcritical in any state by measurements. In the previous research, we have proposed a procedure in which the core safely and efficiently approaches the target subcriticality before the operation. In this procedure, the reference value of the subcriticality at the initial state is measured by the area ratio method capable of the absolute value measurement. The area ratio method uses a pulsed neutron source. However, specific and practical parameters of the accelerator for the area ratio method have not been determined. In this study, we determined the accelerator parameters with the consideration of the uncertainties derived by the dead-time of the detector and the statistical error of the count ratio. In addition, we estimate the coating amount of the sample nuclide in the assumption of the use of the fission chambers.
Abe, Takeyasu; Iida, Yoshihisa
Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 20(3), p.236 - 253, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.23(Construction & Building Technology)This paper is a state-of-the-art report on the performance assessment of cementitious and related materials as components of engineered barrier systems for radioactive waste management. In this paper, (1) the concept of safety functions is reviewed as the engineering background of discussion, (2) an overview of the postclosure performance assessment for Belgian low- and intermediate-level short-lived radioactive waste disposal is provided, and (3) a modeling methodology for engineered barrier systems is analyzed using the concept of "mandala for durability mechanics". According to these works, authors present technical suggestions for technical stakeholders of Japanese low-level radioactive waste disposal.
Ariyoshi, Gen; Obayashi, Hironari; Saito, Shigeru; Sasa, Toshinobu
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/03
To clarify the flow characteristics of heavy liquid-metal (HLM) is important to achieve the construction of nuclear transmutation facility that utilizes HLM as a spallation target and coolant. At present, lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) spallation target plans to be installed in Japan proton accelerator research complex (J-PARC). LBE is also selected as one of the candidate media of a spallation target and a coolant for innovative nuclear systems such as accelerator-driven system (ADS) and LBE-cooled fast reactor, due to its adequate physical/chemical properties. The characteristics of LBE flowing inside the target are usually clarified with computational fluid dynamics analysis since the measurement techniques for the HLM flow are not well established, especially for high temperature region over 450 C that is delivered from ADS's criteria. Therefore, the objective of this study is to develop measurement method for flow characteristics in the high temperature LBE. A miniature electro-magnet is introduced to electro-magnetic probe to overcome the limitation caused by a curie temperature of permanent magnet. To evaluate performance of the new probe, experimental apparatus equipping annular rotating vessel were also manufactured. The new probe was applied to high temperature LBE up to 480
C that is delivered from ADS's criteria. Therefore, the objective of this study is to develop measurement method for flow characteristics in the high temperature LBE. A miniature electro-magnet is introduced to electro-magnetic probe to overcome the limitation caused by a curie temperature of permanent magnet. To evaluate performance of the new probe, experimental apparatus equipping annular rotating vessel were also manufactured. The new probe was applied to high temperature LBE up to 480 C. As a result, proportional induced voltage to the rotation speed of LBE were clearly observed, where excitation currents of the miniature electro-magnet were 0.2 A or 1 A. In this paper, configuration and performance of the newly developed electro-magnet probe to the high temperature LBE will be presented.
C. As a result, proportional induced voltage to the rotation speed of LBE were clearly observed, where excitation currents of the miniature electro-magnet were 0.2 A or 1 A. In this paper, configuration and performance of the newly developed electro-magnet probe to the high temperature LBE will be presented.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita; Yee-Rendon, B.; Katano, Ryota; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Maekawa, Fujio
JAEA-Research 2021-012, 58 Pages, 2022/01
A radiation shielding analysis was performed for the structure located above the spallation target of an accelerator-driven system (ADS), assuming one cycle of an 800 MW thermal and 30 MW beam power operation. In this analysis, the Monte Carlo particle transport code PHITS and the activation analysis code DCHAIN-PHITS were used. The structures to be analyzed are a beam duct above the target, a beam transport room located above the ADS reactor vessel, beam transport equipment, and the room ceiling. For each structure, the radiation doses and radioactivities during and after the operation were estimated. Furthermore, the shielding structure of the ceiling was determined. As a result, it was found that the radiation dose at the site boundary would be sufficiently lower than the legal limit by applying the determined shielding structure. Moreover, under the condition of this study, it was shown that the effective dose rate around the beam transport equipment positioned above the target after the operation exceeded 10 mSv/h, and that the maintenance and replacement of the equipment in the room would require remote handling.
Sasa, Toshinobu
Kasokuki, 18(4), p.233 - 240, 2022/01
Lead bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is a promising option as a spallation target for accelerator-driven transmutation systems (ADS) to reduce the radiological toxicity from long-lived radioactive waste. LBE is a heavy metal and has suitable characteristics both as a spallation target and as a coolant for transmutation systems. However, LBE is also known as a highly corrosive with structural materials. In this paper, technological developments to overcome the issue, the latest research activities such as hightemperature operation and oxygen concentration control to ensure corrosion resistance, are introduced together with the outline of the target for ADS.
Shibata, Ryodai; Yamazaki, Katsuyuki; Yamada, Hiroyuki; Miyaji, Noriko; Nakamura, Hironobu
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
Physical protection systems (PPS) operated for security in nuclear facilities uses computer-controlled systems. If malicious peoples change program or install computer virus to PPS, they are invalidated. Due to insufficient surveillance etc., and then unauthorized removal and sabotage may be caused. This paper introduces efforts of necessary procurement and quality managements etc., for decreasing there affect, and their details.
Tamura, Fumihiko
Kasokuki, 18(3), p.151 - 160, 2021/10
The LLRF control system for the J-PARC RCS plays an important role in acceleration of high intensity beams. The original system had been working well without significant problems for more than a decade, however, the long term maintenance became difficult due to the obsolesce of the old FPGAs in the system. Therefore we developed and deployed the next-generation LLRF control system. The next-generation system is based on the modern platform, MTCA.4. The most important new function of the system is the multiharmonic vector rf voltage control feedback, which compensate the heavy beam loading in the wideband cavity better than the feedforward at the beam intensity of the design beam power, 1MW. The commissioning results are reported. The next-generation system has been successfully deployed.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Okita, Hidefumi; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Shimada, Taihei; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Hara, Keigo*; et al.
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.170 - 174, 2021/10
A stable and precise LLRF (Low Level RF) control system is indispensable for acceleration of high intensity proton beam in the J-PARC RCS. The original LLRF control system had been operated without major problems for more than ten years since the start of operation of the RCS, while maintenance of the system became difficult due to the obsolesce of the old FPGAs in the modules. We developed and installed the next-generation LLRF control system based on MTCA.4. The key function of the system is the multiharmonic vector rf voltage control feedback. We describe the system overview and the commissioning results. The performance of the beam loading compensation is significantly improved.
Nemoto, Miho*; Ebine, Noriya; Okamoto, Akiko; Hosaka, Yasuhisa*; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Terada, Hiroaki; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Technology 2021-013, 41 Pages, 2021/08
When North Korea has carried out nuclear tests, Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center (NEAT) predicts atmospheric dispersion of radionuclides by using the WSPEEDI-II upon requests from Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA) and submits the predicted results to NRA in cooperation with Nuclear Science and Engineering Center (NSEC). This is a part of the activity of NEAT supporting the Japanese Government in emergency responses. The WSPEEDI-II automatic calculation system specialized for responses to nuclear tests by North Korea was developed by NSEC and was used for responses to three nuclear tests from February 2013 to September 2017. This report describes the transfer and installation of the calculation system to NEAT, and the subsequent maintenance and operation. Future issues for responses to nuclear tests are also described in this report.
Ogata, Takanari*; Takano, Masahide
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 63(7), p.541 - 546, 2021/07
, 63(7), p.541 - 546, 2021/07
This is a commentary on metallic fuels for fast reactors and nitride fuels for minor actinide transmutation in accelerator driven system, as the 4th article of serial lecture on Journal of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan; Concepts and basic designs of various nuclear fuels.